Effective note-taking is a crucial skill for academic success and efficient learning. Good notes help you understand, retain, and review information more effectively. This guide will explore various note-taking methods and provide tips for improving your note-taking practices.
Why Take Effective Notes?
- Enhance Understanding: Well-organized notes help you grasp complex concepts and details.
- Improve Retention: Active engagement during note-taking reinforces memory and recall.
- Facilitate Review: Clear and organized notes make studying and revision more efficient.
Tips for Effective Note-Taking
1. Be Prepared
- Gather Materials: Ensure you have all necessary tools, such as notebooks, pens, or digital devices.
- Review Beforehand: Familiarize yourself with the topic before the lecture or reading to better anticipate and understand the material.
2. Focus on Key Points
- Identify Main Ideas: Concentrate on capturing main concepts, key terms, and important details. Avoid transcribing everything verbatim.
- Use Abbreviations: Develop a system of abbreviations and symbols to speed up your writing and capture more information.
3. Organize Your Notes
- Use Headings and Subheadings: Clearly differentiate between topics and subtopics to make your notes easier to navigate.
- Highlight and Underline: Emphasize key points and terms to draw attention to important information.
4. Review and Revise
- Regularly Review: Revisit and revise your notes shortly after taking them to reinforce learning and fill in any gaps.
- Summarize and Reflect: Write summaries or reflections on the material to consolidate your understanding and identify areas for further study.
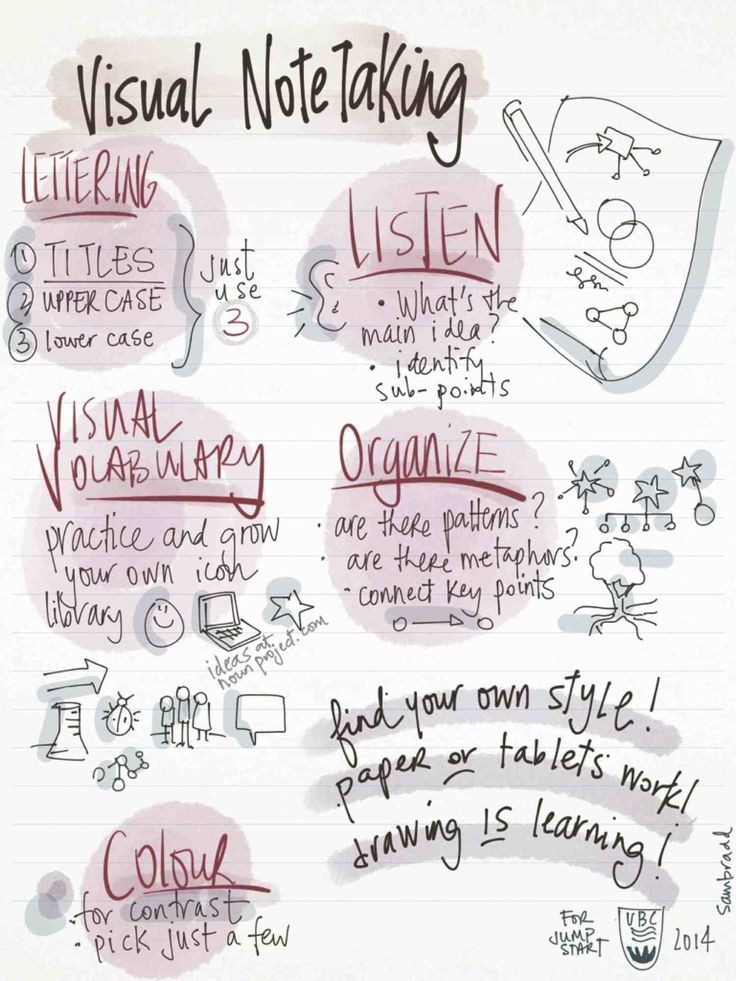
Note-Taking Methods
1. The Cornell Method
- Structure: Divide your page into three sections: a narrow left column (cue), a wider right column (note-taking), and a summary section at the bottom.
- How to Use:
- Note-Taking Column: Record lecture or reading notes in the right column.
- Cue Column: Write key terms, questions, or main ideas in the left column after the lecture.
- Summary: Summarize the notes in your own words at the bottom of the page.

2. The Outline Method
- Structure: Organize notes in a hierarchical structure using bullet points or numbers.
- How to Use:
- Main Topics: Start with main topics as primary headings.
- Subtopics: Add subtopics and details as indented bullet points or numbers beneath each main topic.

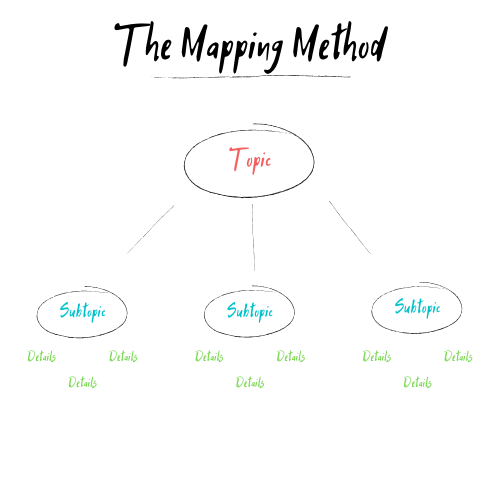
3. The Mapping Method
- Structure: Create a visual diagram that represents the relationships between concepts.
- How to Use:
- Central Idea: Write the central topic in the middle of the page.
- Branches: Draw branches to represent major subtopics and further branches for detailed points.
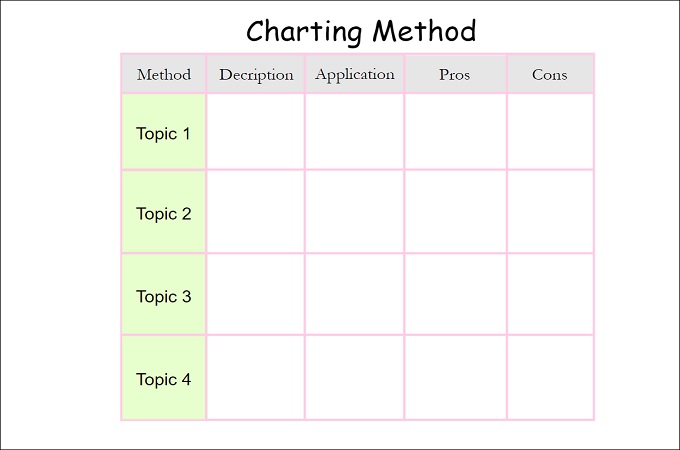
4. The Charting Method
- Structure: Use tables or charts to organize information into categories.
- How to Use:
- Columns and Rows: Create columns for different categories or topics and rows for details or comparisons.
- Organize Data: Fill in the chart with relevant information to facilitate easy comparison and review.
5. The Sentence Method
- Structure: Write notes in a series of sentences that capture the main ideas and details.
- How to Use:
- Define a Topic:
- Condense the Point: Take the point and try summarise it mentally
- Write Sentence: Take the mental summary and write it out as a single sentence underneath the topic heading
- Repeat
- Review and Organize: After the lecture, review and reorganize your notes into a more structured format if needed.



